Interest Rate Swap | Different Types Of Swaps
Size and growth of the swap market An interest rate swap is a contract between two parties to exchange streams of interest payments. An interest rate swap is a legal contract entered into by two parties to exchange cash flows on an agreed upon set of future dates.
Interest Rate Swap An interest rate swap is a derivative contract through which two counterparties agree to exchange one stream of future interest payments for another.
/CurrencySwapBasics-effa071aba184066b9683bf80750c254.png)
Interest rate swap. Contractual arrangement be tween two parties often referred to as counterparties. In most cases interest rate swaps include the exchange of a. What is Interest Rate Swaps.
What is an interest rate swap. These could be interest rates theyre paying on loans or rates theyre receiving on investments. 5 Years Yield Curve.
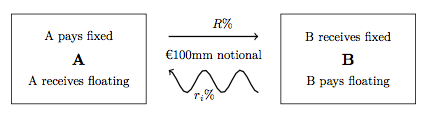
Interest rate swaps have two legs a floating leg FLT and a fixed leg FIX. An interest rate swap is an agreement between two parties to exchange one stream of interest payments for another over a set period of time. An interest rate swap is a contractual agreement between two parties agreeing to exchange cash flows of an underlying asset for a fixed period of time.
An interest rate swap is a type of a derivative contract through which two counterparties agree to exchange one stream of future interest payments for another based on a specified principal amount. A Bank may be able to find a counterparty in more markets than if the company seeking the swap. The floating rate cash.
1 Week1 Month1 Year3 Years. An issuer agree to exchange payments based on a defined principal amount for a fixed period of time. The most common type of interest rate swap arrangement is one in which Party A agrees to make payments to Party B based on the fixed interest rate and Party B agrees to pay party A based on the floating interest rate.
Rate swap is a. In almost all cases the floating. Interest Rate Swaps.
An interest rate swap is a financial contract between two parties such as companies or investors that want to exchange interest rates. Typically one stream of payments is based on a fixed rate of interest and the other stream on a floating rate of interest. An interest rate swap is a financial derivative that companies use to exchange interest rate payments with each other.
Interest rate swap pricing. Currency Swap vs. The most common reason to engage in an interest rate swap is to exchange a variable-rate payment for a fixed-rate payment or vice versa.
An interest rate swap is a forward contract in which one stream of future interest payments is exchanged for another based on a specified principal amount. It is an agreement between two parties to exchange a series of fixed rate cash flows for a. OIS discounting means discounting with EONIA-swaps based curve for EUR and with Fed funds curve for USD interest rate swapsShould be checked for collaterlized swaps If not OIS discounting the.
It also referred to as the reference rate and is typically based on LIBOR. In an interest rate swap the principal amount is not actu. Interest rate swaps An interest rate swap entails the swapping of differing interest obligations between two parties via a facilitator usually a bank that focuses on this market and makes a market in this market.
What is Interest Rate Swap. Basic Interest Rate Swap Mechanics. The notional principal on which the interest payments are.
What is an Interest Rate Swap. A swap may be arranged with a bank or a counter party may be found through a bank or other financial intermediary. Fees will be payable in bank is used.
Libor Rates are available Here. Swaps are derivative contracts between two parties that involve the exchange of cash flows. The term interest rate swap refers to the derivative contract between two parties who agree to exchange one stream of interest payments for another on the basis of a particular pre-determined principal amount.
An interest rate swap allows the parties involved to exchange their interest rate obligations usually a fixed rate for a floating rate to manage interest rate risk or to lower their borrowing costs among other reasons. Current Interest Rate Swap Rates - USD. Only the net cash flows are paid.
Get this FREE widget. As shown in Figure 1 the counterparties in this example a financial institution and. This is the market rate for a given swap structure and termWhile it will differ based on the swap structure a 5-year swap and a 10-year swap will likely have different mid-market rates and may change over time the rate for a 5-year swap is likely different today than what it was.
Interest rate swaps involves two parties agreeing to exchange interest payments over an agreed period of at least one year end typically longer. An interest rate swap is a customized contract between two parties to swap two schedules of cash flows. Swaps are derivative contracts and trade over-the-counter.
The interest rate swaps market constitutes the largest and most liquid part of the global derivatives market. In a nutshell interest rate swap can be said to be a contractual agreement between two parties to exchange interest payments. The rate for a pay-fixed swap consists of two distinct components.
Swaps are useful when one company wants to receive a payment with a variable interest rate while the other wants to limit future risk by receiving a fixed-rate payment instead.

Illustration Showing A Typical Interest Rate Swap With A Pay Leg Of Download Scientific Diagram
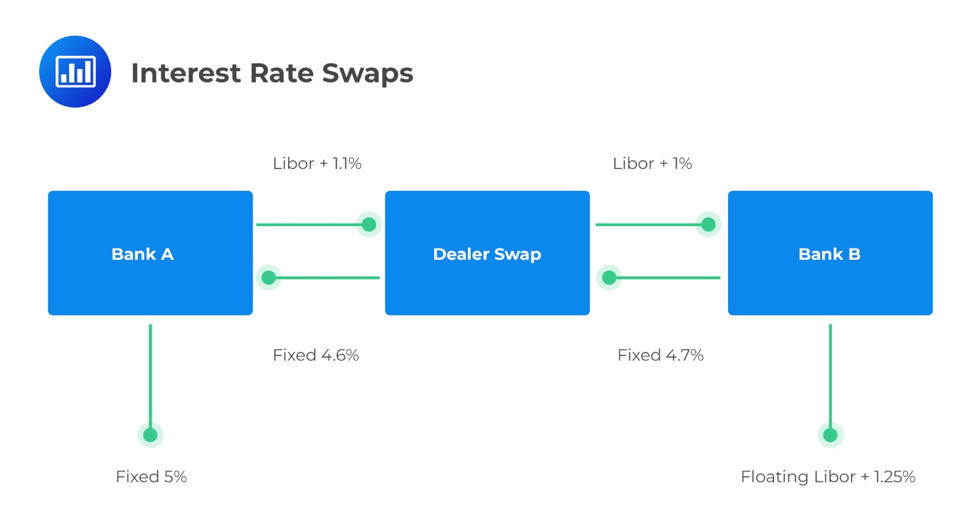
Value And Price Of Swaps Derivatives Cfa Level 1 Exam Analystprep
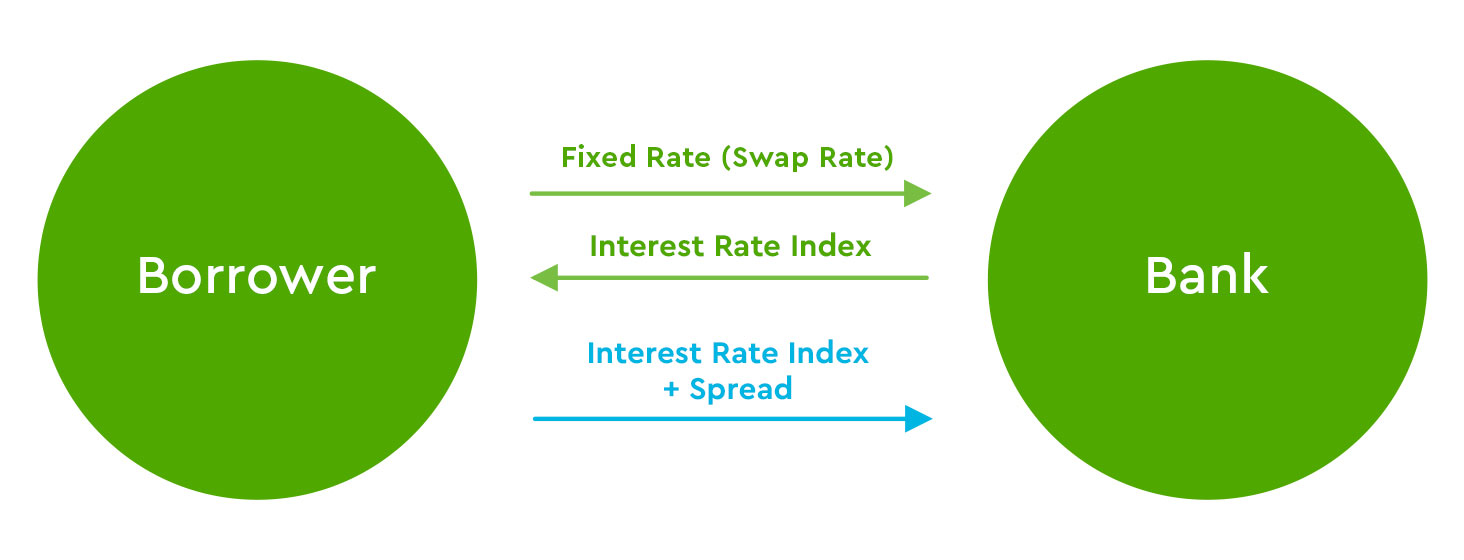
How Interest Rate Swaps Work Commerce Bank
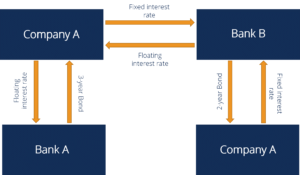
Interest Rate Swap Learn How Interest Rate Swaps Work

Interest Rate Swaps With An Example Youtube
/dotdash_final_Currency_Swap_vs_Interest_Rate_Swap_Whats_the_Difference_Jan_2021-01-d0d9bf99a16c467daeab2fd073b67051.jpg)
Currency Swap Vs Interest Rate Swap
Applied Derivatives Trading Beginners Guide Interest Rate Swaps Irs
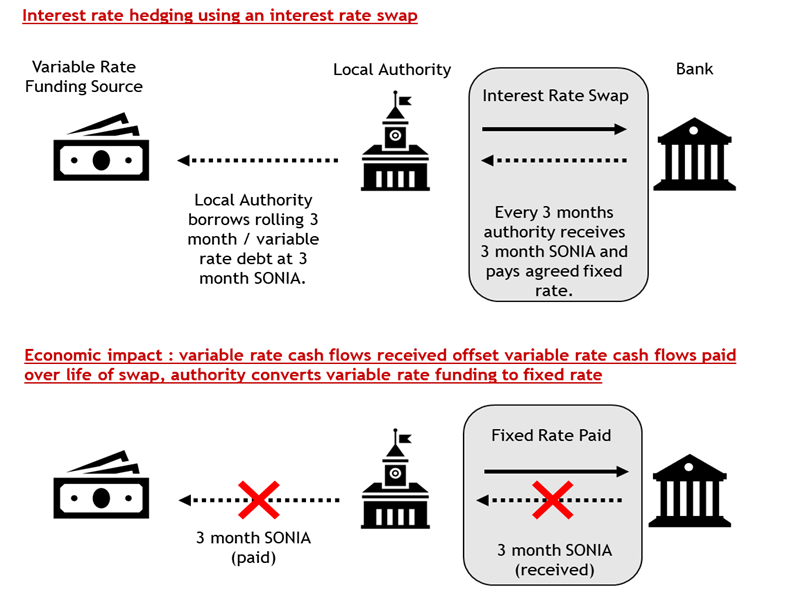
Interest Rate Risk Management Using Swaps
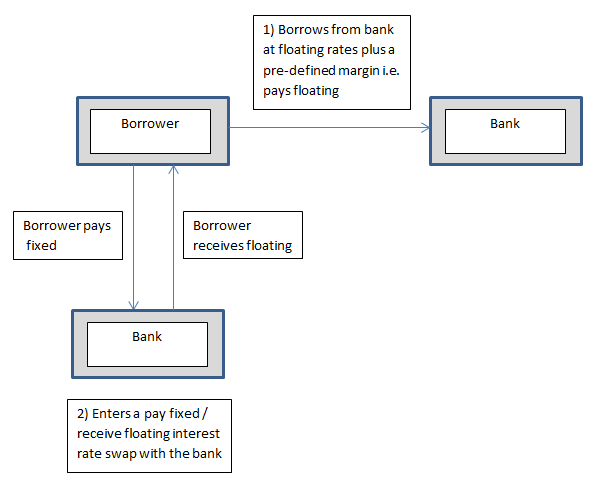
Why Use An Interest Rate Swap And How Does It Work Hedgebook
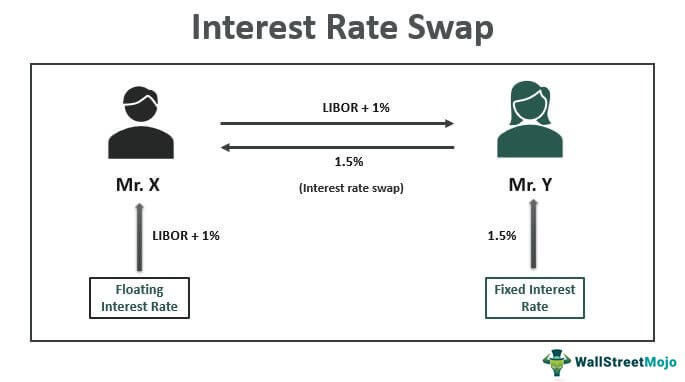
Interest Rate Swap Examples Uses Swap Curve Wsm
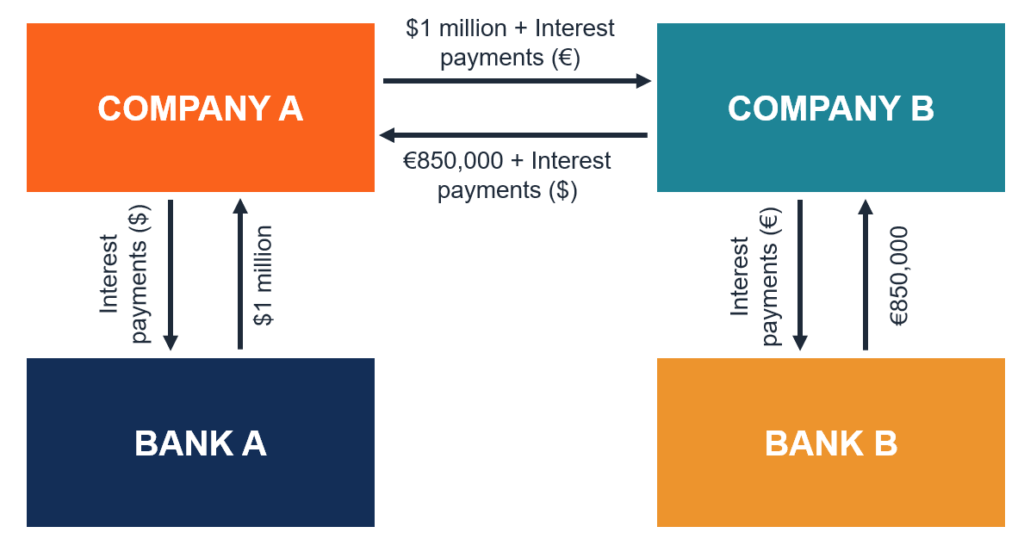
Currency Swap Contract Definition How It Works Types
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_final_Currency_Swap_vs_Interest_Rate_Swap_Whats_the_Difference_Jan_2021-01-d0d9bf99a16c467daeab2fd073b67051.jpg)
Currency Swap Vs Interest Rate Swap

Plain Vanilla Interest Rate Swap Finance Train

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DifferentTypesofSwaps2-4de5ab58b9854ca6b325de77810c3b16.png)
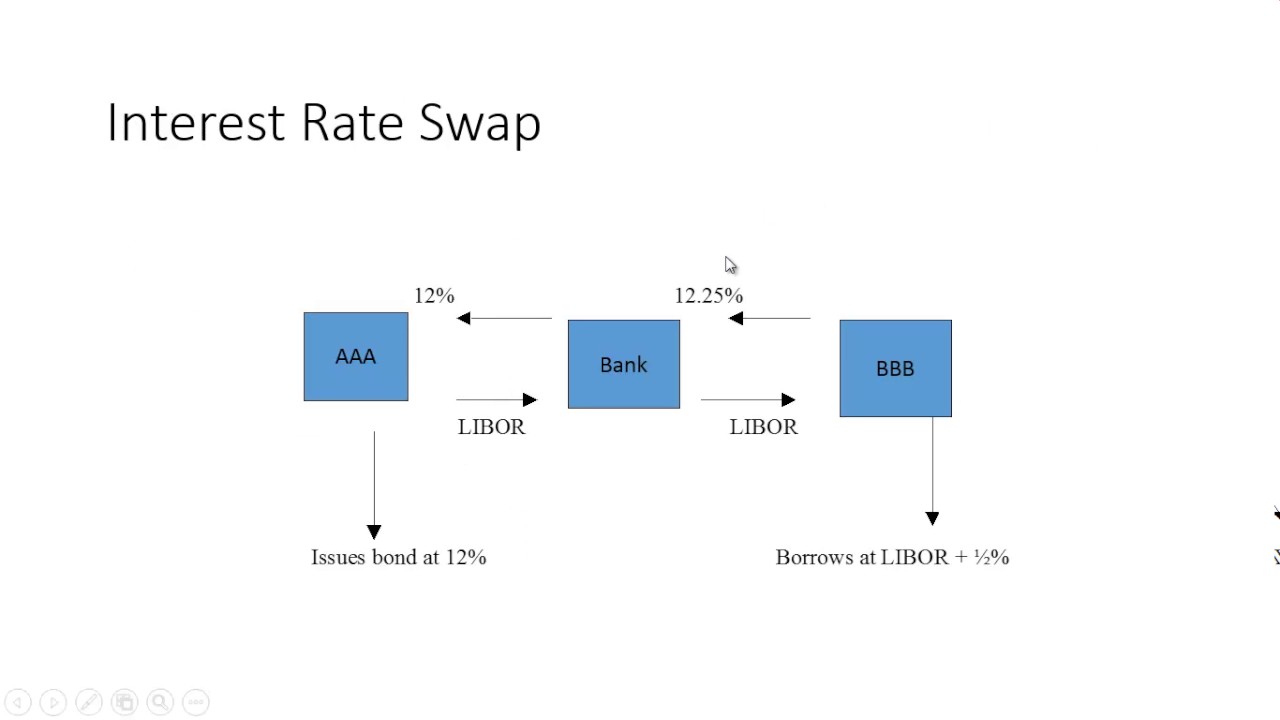

/dotdash_final_Currency_Swap_vs_Interest_Rate_Swap_Whats_the_Difference_Jan_2021-01-d0d9bf99a16c467daeab2fd073b67051.jpg)